AWS Cloud: 7 Powerful Reasons to Dominate the Future
Welcome to the ultimate guide on AWS Cloud—your gateway to scalable, secure, and revolutionary cloud computing. Whether you’re a startup or a global enterprise, discover why millions trust Amazon’s cloud ecosystem.
What Is AWS Cloud and Why It Matters

Amazon Web Services (AWS) Cloud is the world’s most comprehensive and widely adopted cloud platform, offering over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. Launched in 2006, AWS pioneered modern cloud computing, enabling businesses to innovate faster, reduce IT costs, and scale on demand.
The Evolution of Cloud Computing
Before AWS, companies relied on expensive, on-premise data centers. Scaling meant buying more servers, which was slow and capital-intensive. AWS changed that by introducing a pay-as-you-go model, allowing organizations to rent computing power, storage, and databases over the internet.
- Pre-AWS era: High upfront costs, limited scalability
- 2006: AWS launches EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud), S3 (Simple Storage Service)
- Post-2010: Rapid expansion into AI, machine learning, IoT, and serverless computing
“The cloud is not about technology; it’s about business agility.” — Andy Jassy, CEO of Amazon and former AWS CEO
Core Components of AWS Cloud
AWS Cloud is built on a foundation of compute, storage, networking, and security services. These components work together to deliver a flexible, reliable, and secure environment.
- Compute: Services like Amazon EC2, AWS Lambda, and Elastic Beanstalk allow users to run applications at scale.
- Storage: Amazon S3, EBS, and Glacier provide durable, scalable, and cost-effective storage solutions.
- Networking: Amazon VPC, Route 53, and CloudFront enable secure and fast global connectivity.
- Security: IAM, KMS, and Shield protect data and infrastructure with enterprise-grade tools.
Key Benefits of Using AWS Cloud
Organizations choose AWS Cloud not just for its features, but for the tangible business outcomes it delivers. From startups to Fortune 500 companies, AWS empowers innovation and operational efficiency.
Unmatched Scalability and Flexibility
One of the most powerful advantages of AWS Cloud is its ability to scale resources up or down in real time. Whether you’re handling a sudden traffic spike or planning long-term growth, AWS adapts instantly.
- Auto Scaling adjusts capacity based on demand
- Load Balancers distribute traffic across multiple servers
- Global infrastructure spans 33 Availability Zones across 12 geographic regions
This flexibility eliminates over-provisioning and reduces waste, making AWS ideal for dynamic workloads.
Cost Efficiency and Pay-as-You-Go Model
Traditional IT requires massive capital investment. AWS Cloud flips the model: you only pay for what you use. This operational expenditure (OpEx) model improves cash flow and budget predictability.
- No upfront hardware costs
- Reserved Instances offer up to 75% savings for long-term usage
- Spot Instances allow bidding on unused EC2 capacity for up to 90% off
Tools like AWS Cost Explorer and Budgets help monitor and optimize spending, ensuring financial control.
Global Reach and High Availability
AWS operates in 12 geographic regions worldwide, with plans to expand further. This global footprint enables low-latency access and high availability for users across continents.
- Each region has multiple Availability Zones (AZs) for fault tolerance
- Edge locations via Amazon CloudFront accelerate content delivery
- Compliance with local data regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA)
Companies like Netflix and Airbnb rely on AWS’s global network to serve millions of users seamlessly.
AWS Cloud Services: A Deep Dive
AWS offers a vast portfolio of services across categories. Understanding the core offerings helps businesses choose the right tools for their needs.
Compute Services: Powering Your Applications
Compute is the engine of any cloud infrastructure. AWS provides multiple compute options tailored to different use cases.
- Amazon EC2: Virtual servers in the cloud with customizable instance types (e.g., general purpose, memory optimized, GPU instances).
- AWS Lambda: Serverless computing that runs code without provisioning servers. Ideal for event-driven tasks like file processing or API backends.
- Elastic Beanstalk: Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) that simplifies application deployment and management.
These services integrate with monitoring tools like CloudWatch, ensuring performance visibility.
Storage Solutions: Secure and Scalable Data Management
Data is the lifeblood of modern businesses. AWS Cloud offers storage solutions for every need—temporary, persistent, archival, or high-performance.
- Amazon S3: Object storage for backups, media files, and big data analytics. Offers 99.999999999% durability.
- Amazon EBS: Block storage for EC2 instances, ideal for databases and transactional systems.
- Amazon Glacier: Low-cost archival storage for long-term retention and compliance.
S3 also supports versioning, lifecycle policies, and cross-region replication, making it a cornerstone of AWS Cloud strategy.
Networking and Content Delivery
Fast, secure, and reliable networking is critical for cloud performance. AWS provides robust tools to manage connectivity and optimize delivery.
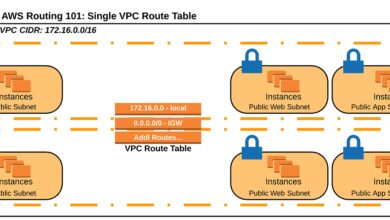
- Amazon VPC: Virtual Private Cloud lets you isolate resources in a private network with custom IP ranges, subnets, and route tables.
- Route 53: Scalable DNS service with health checks and traffic routing policies.
- CloudFront: Content Delivery Network (CDN) that caches content at edge locations, reducing latency for end users.
These services ensure secure, high-speed access to applications, whether internal or public-facing.
Security and Compliance in AWS Cloud
Security is a top priority for AWS. The platform is designed with a shared responsibility model: AWS secures the infrastructure, while customers secure their data and applications.
Shared Responsibility Model Explained
Understanding this model is crucial for effective cloud security.
- AWS Responsibilities: Physical security of data centers, hardware maintenance, network infrastructure, and hypervisor security.
- Customer Responsibilities: Configuring firewalls, managing access controls, encrypting data, and patching guest operating systems.
This division ensures clarity and accountability, empowering organizations to focus on their security posture.
Key Security Services and Tools
AWS provides a suite of tools to enforce security best practices.
- IAM (Identity and Access Management): Controls user access with policies, roles, and multi-factor authentication (MFA).
- KMS (Key Management Service): Manages encryption keys for data at rest and in transit.
- GuardDuty: Threat detection service that monitors for malicious activity using machine learning.
- Security Hub: Centralized dashboard for compliance checks and security findings.
These tools help meet standards like ISO 27001, SOC 1/2/3, and PCI DSS.
Compliance and Data Protection
AWS supports over 140 compliance programs, making it suitable for regulated industries like finance, healthcare, and government.
- HIPAA-compliant services for healthcare data
- GDPR-ready tools for European data privacy
- AWS Artifact for on-demand compliance reports
With built-in encryption and audit trails, AWS Cloud ensures data protection by design.
AWS Cloud for Developers and DevOps
For developers, AWS Cloud is a playground of innovation. It streamlines development workflows, accelerates testing, and enables continuous delivery.
Developer Tools and SDKs
AWS provides extensive tools to support coding, debugging, and deployment.
- AWS CLI and SDKs: Command-line interface and software development kits for Python, Java, .NET, and more.
- CodeCommit: Fully managed source control service for Git repositories.
- CodeBuild: Automated build service that compiles source code and runs tests.
- CodeDeploy: Automates application deployments to EC2, on-premises, or Lambda.
These tools integrate seamlessly into CI/CD pipelines, boosting developer productivity.
Serverless Architecture with AWS Lambda
Serverless computing is revolutionizing how apps are built. AWS Lambda allows developers to run code without managing servers.
- Code executes in response to events (e.g., S3 uploads, API calls)
- No server management, automatic scaling, and per-millisecond billing
- Integrates with API Gateway, DynamoDB, and SNS
Use cases include chatbots, real-time file processing, and backend APIs. Learn more at AWS Lambda Official Page.
DevOps and Automation with AWS
DevOps teams leverage AWS to automate infrastructure and streamline operations.
- CloudFormation: Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tool to model and provision AWS resources using JSON or YAML templates.
- OpsWorks: Configuration management with Chef and Puppet.
- Systems Manager: Centralized operations across EC2, on-premises, and hybrid environments.
Automation reduces human error, improves consistency, and accelerates deployment cycles.
Real-World Use Cases of AWS Cloud
AWS Cloud powers some of the world’s most innovative companies. Let’s explore how different industries leverage its capabilities.
Netflix: Streaming at Global Scale
Netflix migrated its entire video streaming platform to AWS Cloud, handling over 250 million subscribers worldwide.
- Uses EC2 for compute, S3 for video storage, and CloudFront for content delivery
- Lambda processes metadata and thumbnails
- Reduces downtime and scales during peak viewing hours
This migration allowed Netflix to innovate rapidly and enter new markets quickly.
NASA: Space Exploration and Data Analytics
NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) uses AWS Cloud for processing satellite imagery and Mars rover data.
- Processes petabytes of Earth observation data using Amazon S3 and EMR
- Runs machine learning models to detect wildfires and climate patterns
- Public datasets available via AWS Open Data Registry
Learn more at NASA on AWS Case Study.
Siemens: Industrial IoT and Smart Manufacturing
Siemens uses AWS Cloud to power its MindSphere IoT platform, connecting industrial machines and analyzing performance data.
- Collects sensor data from turbines, trains, and factories
- Uses AWS IoT Core and Kinesis for real-time data ingestion
- Applies predictive maintenance with SageMaker
This reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency across global operations.
Migrating to AWS Cloud: Best Practices
Migrating to AWS Cloud can be complex, but following best practices ensures a smooth transition.
Assessment and Planning
Before migration, assess your current environment and define goals.
- Use AWS Application Discovery Service to inventory on-premises servers
- Define migration strategy: rehost (lift-and-shift), refactor, rearchitect, or replace
- Estimate costs with AWS TCO Calculator
Planning reduces risks and aligns stakeholders.
Execution and Monitoring
Use AWS migration tools to streamline the process.
- Server Migration Service (SMS): Replicates on-premises VMs to AWS
- Database Migration Service (DMS): Migrates databases with minimal downtime
- CloudEndure: Real-time replication for disaster recovery and migration
Monitor progress with CloudWatch and Trusted Advisor.
Post-Migration Optimization
After migration, focus on optimization and governance.
- Right-size EC2 instances to avoid over-provisioning
- Enable auto-scaling and load balancing
- Implement tagging policies for cost allocation
- Use AWS Well-Architected Framework to review architecture
Continuous improvement ensures long-term success.
Future Trends in AWS Cloud
AWS continues to innovate, shaping the future of cloud computing.
AI and Machine Learning Integration
AWS SageMaker democratizes machine learning, enabling developers to build, train, and deploy models at scale.
- Pre-built algorithms and Jupyter notebooks
- AutoML for automated model tuning
- Integration with Alexa, Rekognition, and Comprehend
Industries from retail to healthcare are leveraging AI for personalization and automation.
Edge Computing with AWS Wavelength and Outposts
To reduce latency, AWS brings compute closer to users.
- AWS Wavelength: Embeds AWS services within 5G networks for mobile applications
- AWS Outposts: Runs AWS infrastructure on-premises for hybrid workloads
- Supports real-time applications like AR/VR, autonomous vehicles, and industrial automation
This blurs the line between cloud and edge, enabling next-gen applications.
Sustainability and Green Cloud Computing
AWS is committed to sustainability, aiming for 100% renewable energy by 2025.
- Energy-efficient data centers with advanced cooling
- Carbon footprint tool to track emissions
- Supports customers in achieving their ESG goals
Green cloud computing is not just ethical—it’s economically smart.
Getting Started with AWS Cloud
Ready to begin your AWS journey? Here’s how to get started.
Create an AWS Account
Visit aws.amazon.com and sign up for a free account. You’ll get access to the AWS Free Tier, which includes 12 months of free services and always-free offerings like Lambda and S3.
Explore the AWS Management Console
The AWS Management Console is your central hub for managing services. It features a user-friendly dashboard, service catalog, and billing dashboard.
- Navigate using the search bar or service menu
- Use Regions to select geographic locations
- Monitor usage and costs in the Billing & Cost Management dashboard
Leverage Free Learning Resources
AWS offers extensive training to help you build skills.
- AWS Training and Certification: Free digital courses and paid certifications (e.g., AWS Certified Solutions Architect)
- AWS Educate: Free access for students and educators
- AWS re:Invent: Annual conference with technical sessions and keynotes
Start with the AWS Getting Started Guide to launch your first EC2 instance or S3 bucket.
What is AWS Cloud used for?
AWS Cloud is used for hosting websites, running applications, storing data, analyzing big data, deploying machine learning models, and enabling DevOps automation. It supports virtually every IT function in modern organizations.
Is AWS Cloud free?
AWS offers a Free Tier with 12 months of free usage for new customers, plus always-free services like AWS Lambda and Amazon S3 (up to certain limits). Most services are pay-as-you-go, so you only pay for what you use.
How secure is AWS Cloud?
AWS Cloud is highly secure, with data centers protected by physical and digital safeguards. It supports encryption, identity management, and compliance with global standards. Security is a shared responsibility between AWS and the customer.
What are the main competitors of AWS Cloud?
Main competitors include Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Platform (GCP), and Oracle Cloud. However, AWS leads in market share, service breadth, and global infrastructure.
How do I learn AWS Cloud?
You can learn AWS through free resources like AWS Training and Certification, AWS Educate, and hands-on labs. Earning certifications like AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner or Solutions Architect validates your expertise and boosts career prospects.
AWS Cloud is more than just a technology platform—it’s a catalyst for innovation, efficiency, and growth. From startups to global enterprises, AWS empowers organizations to build, deploy, and scale applications like never before. With its vast service portfolio, global infrastructure, and relentless innovation, AWS remains the leader in cloud computing. Whether you’re migrating legacy systems, building AI-driven apps, or optimizing costs, AWS Cloud provides the tools and flexibility to succeed. The future is in the cloud, and AWS is leading the way.
Further Reading: