AWS Beanstalk: 7 Powerful Benefits You Can’t Ignore
Ever felt overwhelmed trying to deploy apps on the cloud? AWS Beanstalk makes it simple, powerful, and surprisingly intuitive—letting developers focus on code, not infrastructure.
What Is AWS Beanstalk and Why It Matters

AWS Elastic Beanstalk, commonly referred to as AWS Beanstalk, is a Platform as a Service (PaaS) offering from Amazon Web Services (AWS) that simplifies the deployment, scaling, and management of web applications. It’s designed for developers who want to launch applications quickly without diving deep into the complexities of underlying infrastructure.
Core Definition and Purpose
AWS Beanstalk abstracts away the heavy lifting of server provisioning, load balancing, auto-scaling, and health monitoring. You simply upload your code, and Beanstalk automatically handles the deployment across AWS resources like EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Elastic Load Balancers.
- Supports multiple languages: Java, .NET, PHP, Node.js, Python, Ruby, Go, and Docker.
- Automatically provisions and configures AWS resources based on application needs.
- Integrates seamlessly with other AWS services like CloudWatch, S3, and IAM.
This abstraction allows developers to focus on writing code rather than managing servers, making it ideal for startups and agile development teams.
How AWS Beanstalk Fits Into the AWS Ecosystem
While AWS offers Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) tools like EC2 and VPC, AWS Beanstalk operates at a higher level of abstraction. It leverages these foundational services but hides their complexity behind a user-friendly interface.
“AWS Elastic Beanstalk enables you to quickly deploy and manage applications in the AWS Cloud without having to learn about the infrastructure that runs those applications.” — AWS Official Documentation
It acts as a bridge between raw infrastructure and fully managed services like AWS Lambda. This makes it perfect for applications that need more control than serverless allows but less overhead than managing EC2 instances manually.
For example, when you deploy an app using AWS Beanstalk, it automatically creates an EC2 instance, attaches it to an Elastic Load Balancer, sets up Auto Scaling groups, and configures CloudWatch monitoring—all without requiring manual intervention.
Key Features That Make AWS Beanstalk Stand Out
AWS Beanstalk isn’t just another deployment tool—it’s packed with intelligent features that streamline the entire application lifecycle. From automatic scaling to integrated monitoring, it’s built for real-world use cases.
Automatic Scaling and Load Balancing
One of the most powerful aspects of AWS Beanstalk is its ability to scale your application automatically based on traffic. You can define scaling policies based on CPU usage, network traffic, or custom CloudWatch metrics.
- Horizontal scaling: Adds or removes EC2 instances based on demand.
- Vertical scaling: Can be configured with instance type changes during peak loads.
- Integrated Elastic Load Balancer (ELB) distributes traffic across healthy instances.
This ensures your application remains responsive during traffic spikes without manual intervention. For instance, an e-commerce site during Black Friday can scale up automatically and scale down when traffic normalizes, saving costs.
Learn more about scaling options in the AWS Auto Scaling documentation.
Environment Management and Configuration
AWS Beanstalk allows you to create multiple environments for different stages of development—like development, staging, and production. Each environment runs independently with its own resources and configurations.
- Environment types: Web server environments and worker environments (for background tasks).
- Configuration templates let you save and reuse settings across environments.
- Rolling updates and immutable deployments minimize downtime during updates.
This flexibility supports DevOps practices like CI/CD, enabling teams to test changes safely before rolling them out to production.
For example, you can deploy a new version to a staging environment, run automated tests, and then promote it to production with a single command.
Supported Platforms and Language Runtimes
AWS Beanstalk supports a wide range of programming languages and platforms, making it accessible to diverse development teams. Whether you’re building a Python Flask app or a .NET Core service, Beanstalk has you covered.
Programming Languages and Frameworks
The platform officially supports the following runtimes:
- Java (Tomcat, Java SE)
- .NET on Windows Server
- PHP (Apache)
- Node.js
- Python (WSGI, Flask, Django)
- Ruby (Passenger, Puma)
- Go
- Docker (single container or multi-container via ECS)
This broad support means developers don’t need to change their tech stack to use AWS Beanstalk. You can deploy a Django app just as easily as a Node.js microservice.
Each platform includes preconfigured Docker images and deployment scripts, reducing setup time significantly.
Custom Platforms and Docker Integration
For teams using niche or custom runtimes, AWS Beanstalk allows the creation of custom platforms using Packer and EC2 Image Builder. This gives full control over the underlying OS and software stack.
- Custom platform definitions can include specific libraries, security patches, or monitoring agents.
- Docker support enables containerized applications with either single or multi-container environments.
- Multi-container Docker environments use Amazon ECS under the hood for orchestration.
This makes AWS Beanstalk suitable not only for traditional apps but also for modern container-based architectures.
Check out the Custom Platforms guide for more details on building your own.
Deployment Strategies and CI/CD Integration
Deploying applications efficiently is critical in modern development. AWS Beanstalk offers several deployment strategies and integrates smoothly with CI/CD pipelines.
Available Deployment Policies
AWS Beanstalk supports multiple deployment methods to suit different risk tolerances and availability requirements:
- All at once: Deploys to all instances simultaneously. Fast but risky—downtime possible.
- Rolling: Updates instances in batches, minimizing downtime.
- Rolling with additional batch: Adds extra capacity during deployment to maintain performance.
- Immutable: Launches a new fleet of instances with the new version; swaps traffic after testing. Zero-downtime guarantee.
- Blue/Green: Uses environment swapping for seamless transitions between versions.
Immutable and blue/green deployments are especially valuable for production environments where uptime is critical.
For example, a financial application might use immutable deployments to ensure that every update is tested on a clean environment before going live.
Integrating with CI/CD Tools
AWS Beanstalk works seamlessly with popular CI/CD tools like Jenkins, GitHub Actions, AWS CodePipeline, and CircleCI.
- CodePipeline can automate the entire flow: build → test → deploy to Beanstalk.
- GitHub Actions can trigger deployments directly from a push to the main branch.
- Jenkins plugins allow integration with existing pipelines.
This integration enables automated testing and deployment, reducing human error and accelerating release cycles.
See the AWS CodePipeline tutorial for setting up a full CI/CD pipeline with Beanstalk.
Monitoring, Logging, and Debugging in AWS Beanstalk
Once your application is live, monitoring its health and performance is crucial. AWS Beanstalk provides robust tools for real-time insights and troubleshooting.
Built-in Monitoring with CloudWatch
Every Beanstalk environment sends metrics to Amazon CloudWatch, including:
- CPU utilization
- Network in/out
- Request count
- Latency
- HTTP 4xx and 5xx error rates
You can set alarms based on these metrics to get notified of issues. For example, if CPU usage exceeds 80% for 5 minutes, an SNS notification can alert your team.
CloudWatch also captures logs from your application and web server, which can be streamed to CloudWatch Logs for long-term retention and analysis.
“Monitoring is not optional—it’s essential. AWS Beanstalk makes it effortless.”
Log Access and Troubleshooting Tools
Debugging issues in production is simplified with Beanstalk’s log management features:
- Download full logs (web server, application, and system) directly from the AWS Console.
- Enable log streaming to automatically send logs to CloudWatch.
- Use the
eb logscommand in the EB CLI to fetch logs locally.
Additionally, the AWS Management Console provides a health dashboard showing instance status, request rates, and latency trends.
If an instance fails a health check, Beanstalk can automatically replace it, ensuring high availability.
Cost Management and Resource Optimization
While AWS Beanstalk simplifies deployment, understanding its cost implications is vital for budget control. Since Beanstalk is a free service, you only pay for the underlying AWS resources it uses.
Understanding the Pricing Model
AWS Beanstalk itself does not charge any additional fees. However, the resources it provisions—such as EC2 instances, EBS volumes, ELB, and S3 storage—are billed at standard AWS rates.
- EC2 instances: Billed per second (Linux) or per hour (Windows).
- Elastic Load Balancer: Charged per hour and data processed.
- S3: Minimal cost for storing application versions and logs.
- RDS (if used): Separate billing applies.
For example, a small t3.micro instance with a load balancer might cost around $20–$30 per month, depending on usage.
Use the AWS Pricing Calculator to estimate your monthly costs based on expected traffic and instance types.
Strategies to Reduce Costs
To optimize spending, consider the following best practices:
- Use Auto Scaling to scale down during off-peak hours.
- Delete unused application versions in S3 to reduce storage costs.
- Choose appropriate instance types (e.g., t3.small instead of m5.large if sufficient).
- Use Spot Instances for non-critical environments like staging.
Additionally, enabling detailed billing reports helps track spending by environment or application, making cost allocation easier for teams.
Security and Compliance in AWS Beanstalk
Security is a shared responsibility between AWS and the customer. While AWS secures the infrastructure, you’re responsible for securing your application and configurations.
IAM Roles and Instance Profiles
Every Beanstalk environment uses an IAM instance profile that grants permissions to EC2 instances to interact with other AWS services.
- Best practice: Assign minimal required permissions (principle of least privilege).
- Never hardcode AWS credentials in your application.
- Use IAM roles to allow access to S3, DynamoDB, or SQS as needed.
For example, if your app needs to read from an S3 bucket, attach a policy to the instance profile allowing s3:GetObject on that specific bucket.
Learn more about securing Beanstalk in the IAM Roles for EC2 documentation.
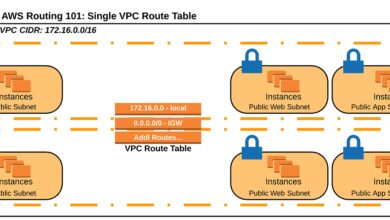
Network Security and VPC Integration
AWS Beanstalk environments can be launched inside a Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for enhanced network isolation.
- Place web servers in public subnets with internet access.
- Run databases in private subnets with no direct internet exposure.
- Use Security Groups to control inbound and outbound traffic.
This setup ensures that sensitive components like RDS instances are protected from public access while still being reachable by your application.
You can also enable HTTPS using Elastic Load Balancer with ACM (AWS Certificate Manager) to encrypt traffic between users and your app.
Common Use Cases and Real-World Applications
AWS Beanstalk is versatile and used across industries for various application types. Its ease of use and scalability make it a go-to choice for many development teams.
Startup Application Deployment
Startups benefit from AWS Beanstalk because it allows rapid deployment with minimal DevOps overhead. Founders can launch MVPs quickly without hiring infrastructure specialists.
- Fast time-to-market: Deploy in minutes, not days.
- Low operational cost: Pay only for what you use.
- Easy scaling: Grow from 10 to 10,000 users seamlessly.
Many Y Combinator startups use Beanstalk for early-stage applications due to its simplicity and AWS integration.
Enterprise Web Applications
Large organizations use AWS Beanstalk to standardize deployment processes across teams. It provides consistency, auditability, and compliance with corporate IT policies.
- Enforce security baselines via configuration templates.
- Integrate with existing monitoring and logging systems.
- Support multiple environments per application (dev, test, prod).
For example, a global bank might use Beanstalk to deploy internal tools across regions while maintaining compliance with financial regulations.
Microservices and API Backends
While Kubernetes is often used for microservices, AWS Beanstalk is a lighter alternative for smaller-scale services.
- Each microservice can run in its own Beanstalk environment.
- Use worker environments to process background jobs from SQS queues.
- Expose APIs via API Gateway or directly through ELB.
This approach reduces complexity compared to managing a full Kubernetes cluster, especially for teams without dedicated DevOps resources.
What is AWS Beanstalk?
AWS Beanstalk is a fully managed PaaS that automates the deployment, scaling, and monitoring of web applications on AWS. You upload your code, and Beanstalk handles the rest using EC2, ELB, Auto Scaling, and other AWS services.
Is AWS Beanstalk free to use?
Yes, AWS Beanstalk itself is free. You only pay for the underlying AWS resources it provisions, such as EC2 instances, load balancers, and storage.
How does AWS Beanstalk differ from AWS Lambda?
Beanstalk is for long-running applications on servers (or containers), while Lambda is for event-driven, short-lived functions (serverless). Beanstalk offers more control; Lambda offers lower operational overhead.
Can I use Docker with AWS Beanstalk?
Yes, AWS Beanstalk supports both single-container and multi-container Docker environments. Multi-container setups use Amazon ECS for orchestration behind the scenes.
Does AWS Beanstalk support blue/green deployments?
Yes, AWS Beanstalk supports blue/green deployments through environment swapping, allowing zero-downtime releases and easy rollback if needed.
In summary, AWS Beanstalk is a powerful, developer-friendly service that bridges the gap between infrastructure control and operational simplicity. Whether you’re launching a startup MVP or managing enterprise applications, it reduces deployment complexity while leveraging the full power of AWS. With automatic scaling, robust monitoring, and seamless CI/CD integration, it remains a top choice for teams looking to ship code faster and more reliably.
Recommended for you 👇
Further Reading: